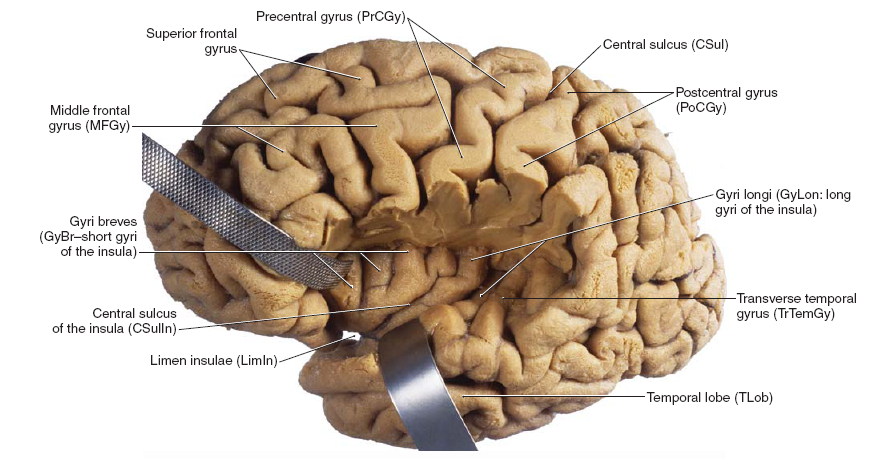
43.MANDIBLE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
Mandible squamous cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that affects the squamous cells lining the mandible (lower jawbone). Here are some clinical points related to this condition:
INTEROSSOUS MEMBRANE BETWEEN TIBIA AND FIBULA
The proximal and distal tibiofibular joints refer to two articulations between the tibia and fibula of the leg. These joints have minimal function in terms of movement but play a greater role in stability and weight-bearing.
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the proximal and distal tibiofibular joints – their structures, neurovascular supply and clinical relevance.
Adapted from work by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
42.MESENTERIC CYST
A mesenteric cyst is a rare condition where a cystic mass develops in the mesentery, the tissue that connects the intestine to the abdominal wall. It is a relatively uncommon finding, and the incidence rate is estimated to be around 1 in 27,000 individuals.
SPLEEN WITH SPLENIC VESSELS
Vasculature
The spleen is a highly vascular organ. It receives most of its arterial supply from the splenic artery. This vessel arises from the coeliac trunk, running laterally along the superior aspect of the pancreas, within the splenorenal ligament. As the artery reaches the spleen, it branches into five vessels – each supplying a different part of the organ.
SPLEEN
Structure
The spleen has a slightly oval shape. It is covered by a weak capsule that protects the organ whilst allowing it to expand in size.
The outer surface of the spleen can be anatomically divided into two:
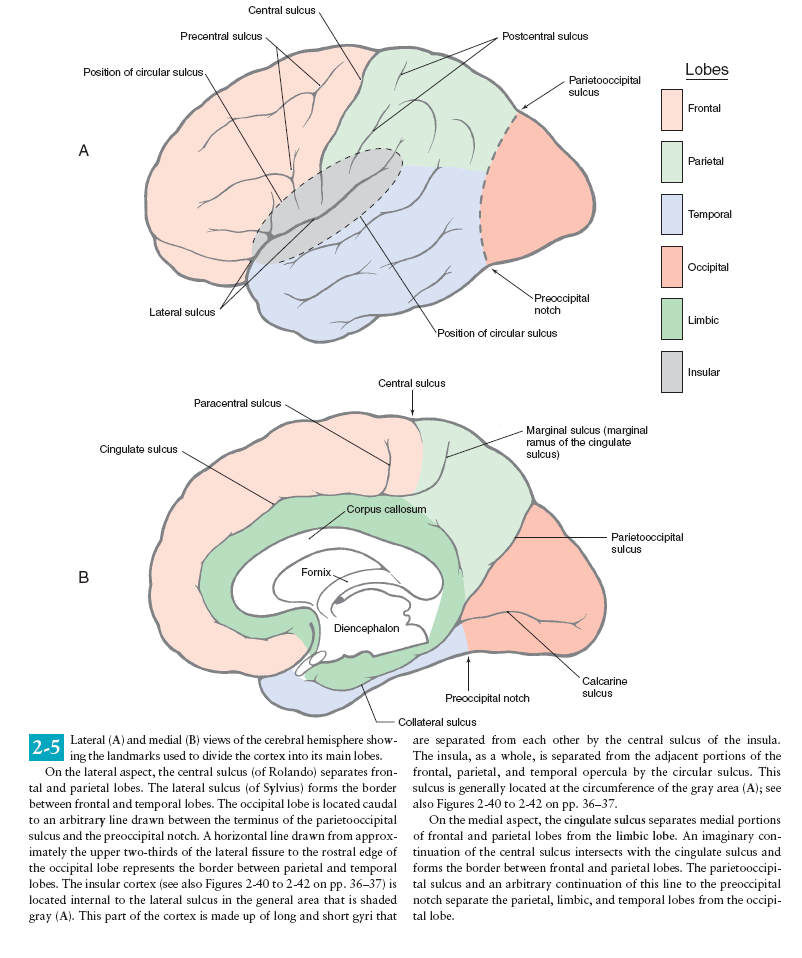
Saggital Section of Brainstem
The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. It is
sited in the posterior cranial fossa, and its ventral surface lies on the clivus.
It contains numerous intrinsic neurone cell bodies and their processes, some
of which are the brain stem homologues of spinal neuronal groups. These
include the sites of termination and cells of origin of axons that enter or leave
the brain stem through the cranial nerves. They provide the sensory, motor
and autonomic innervation of structures that are mostly in the head and
SPLEEN
The spleen is an organ located in the upper left abdomen, and is roughly the size of a clenched fist. In the adult, the spleen functions mainly as a blood filter, removing old red blood cells. It also plays a role in both cell-mediated and humoral immune responses.
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the spleen – its anatomical position, structure and vasculature.
By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2023)
MUSCLES OF THIGH WITH GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
The gluteal region is an anatomical area located posteriorly to the pelvic girdle, at the proximal end of the femur. The muscles in this region move the lower limb at the hip joint.
The muscles of the gluteal region can be broadly divided into two groups:
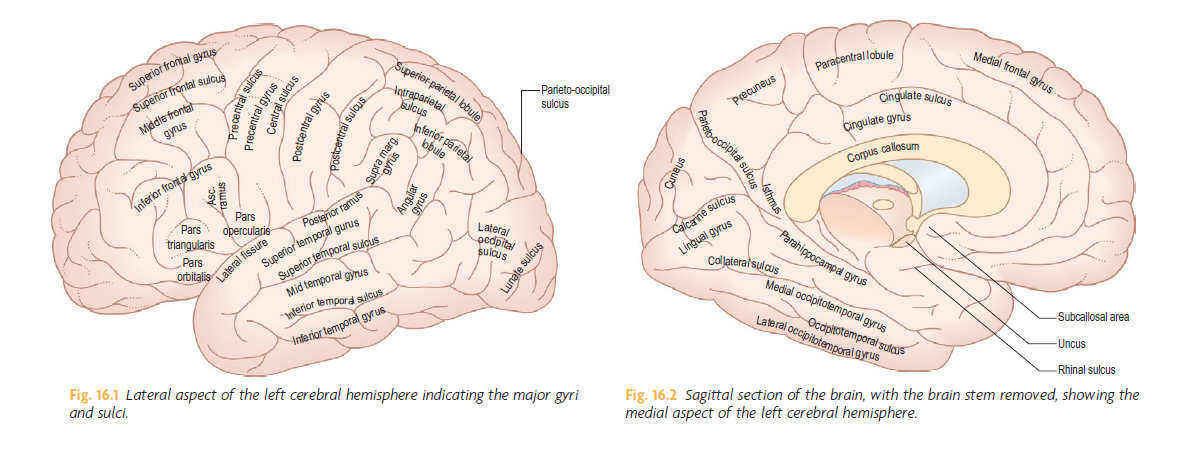
Saggital Section of Brain
https://youtu.be/2ztESvDnxT0