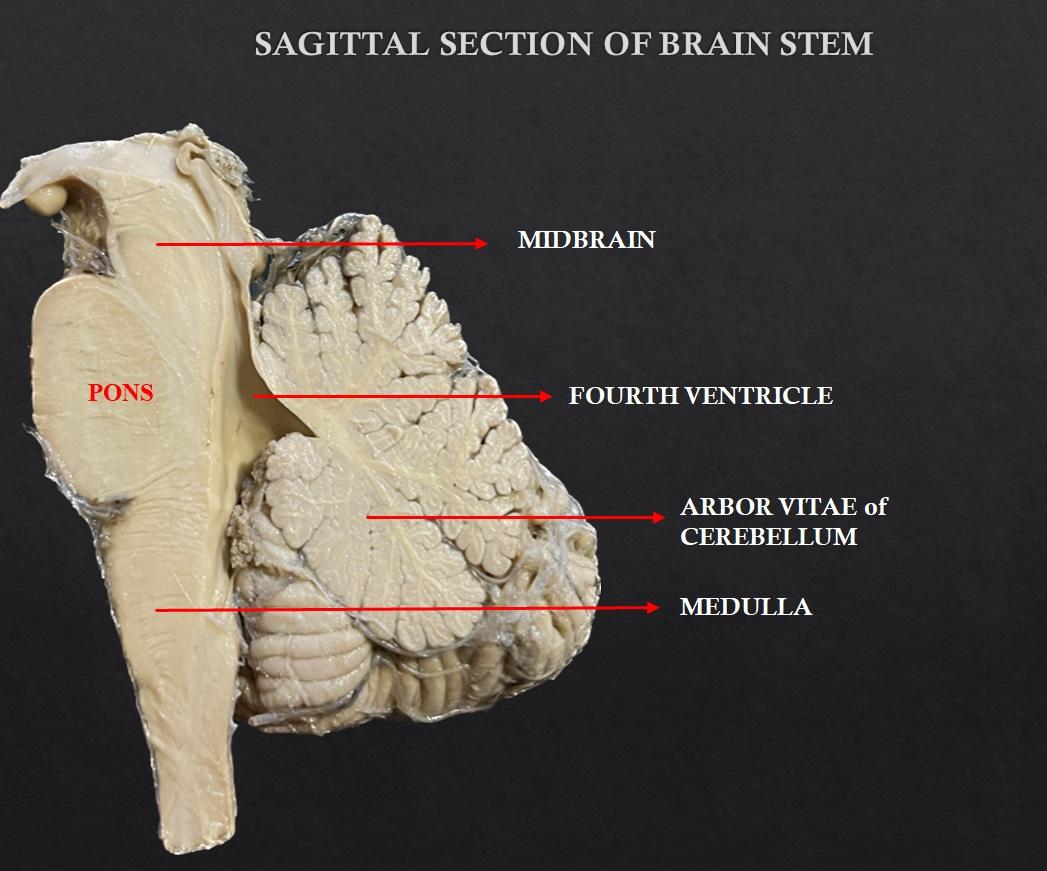
The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. It is
sited in the posterior cranial fossa, and its ventral surface lies on the clivus.
It contains numerous intrinsic neurone cell bodies and their processes, some
of which are the brain stem homologues of spinal neuronal groups. These
include the sites of termination and cells of origin of axons that enter or leave
the brain stem through the cranial nerves. They provide the sensory, motor
and autonomic innervation of structures that are mostly in the head and
neck. Autonomic fibres, which arise from the brain stem, are distributed more
widely. Additional groups of neurones receive input related to the special
senses of hearing, vestibular function and taste. The reticular formation
is an extensive and often ill-defined network of neurones that extends
throughout the length of the brain stem and is continuous caudally with its
spinal counterpart. Some of its nuclei are concerned with cardiac, respiratory
and alimentary control; some are involved in aspects of many neural activities,
and others provide or receive massive afferent and efferent cerebellar
projections.
The brain stem is the site of termination of numerous ascending and
descending fibres and is traversed by many others. The spinothalamic (spinal
lemniscal), medial lemniscal and trigeminal systems ascend through the brain
stem to reach the thalamus. Prominent corticospinal
projections descend through the brain stem, and corticobulbar projections
end within it.
Clinically, damage to the brain stem is often devastating and life threatening.
This is because it is a structurally and functionally compact region, where
even small lesions can destroy vital cardiac and respiratory centres, disconnect
forebrain motor areas from brain stem and spinal motor neurones and
sever incoming sensory fibres from higher centres of consciousness, perception
and cognition. Irreversible cardiac and respiratory arrest follows complete
destruction of the neural respiratory and cardiac centres in the medulla.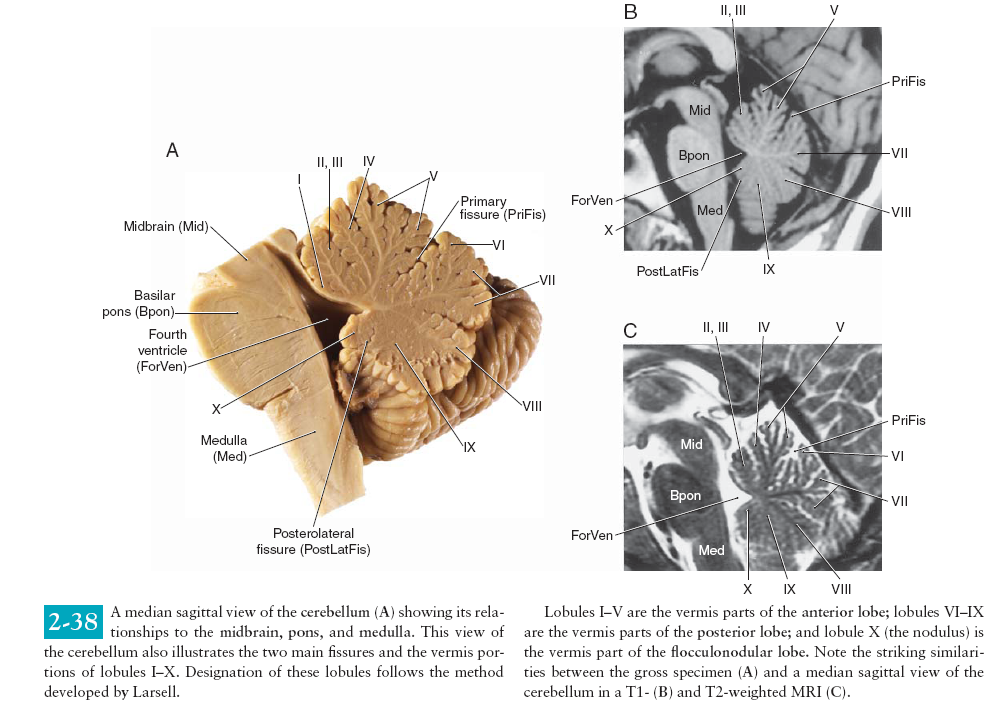
https://youtu.be/Mkj78h8w4a8