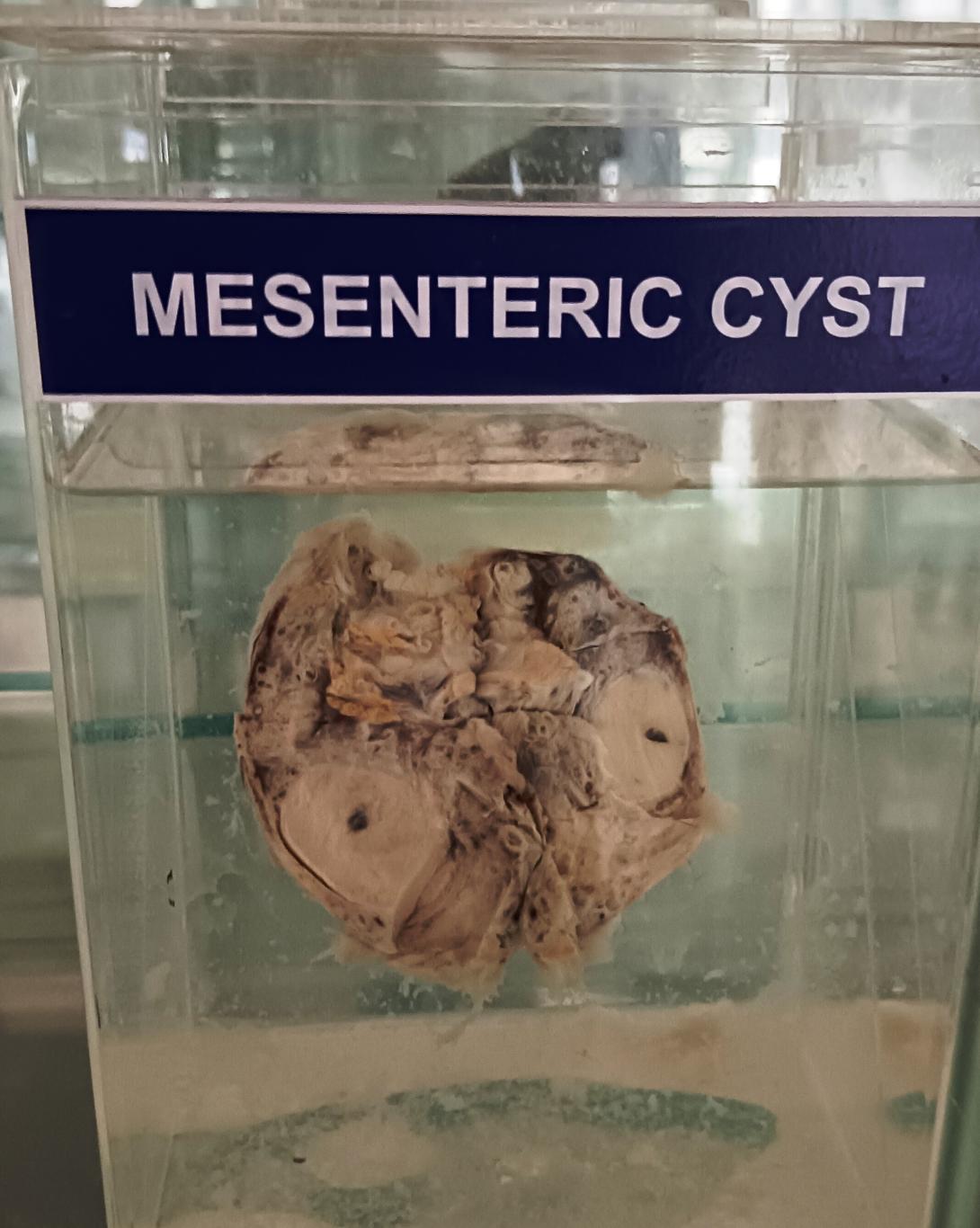
A mesenteric cyst is a rare condition where a cystic mass develops in the mesentery, the tissue that connects the intestine to the abdominal wall. It is a relatively uncommon finding, and the incidence rate is estimated to be around 1 in 27,000 individuals.
The exact cause of mesenteric cysts is not known, but it is believed to be related to developmental abnormalities in the lymphatic system during embryonic development. Mesenteric cysts are usually asymptomatic and are often discovered incidentally during routine imaging studies or during investigations for other abdominal conditions.
When symptoms occur, they can include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and bowel obstruction. In some cases, the cyst may become infected or rupture, which can lead to more severe symptoms such as fever and sepsis.
Diagnosis of a mesenteric cyst is typically made through imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. Treatment options for mesenteric cysts depend on the size and location of the cyst, as well as the presence of any symptoms. In general, small asymptomatic cysts may not require treatment and can be monitored through regular imaging studies. Surgical removal of the cyst may be necessary in cases where the cyst is large, causing symptoms or there is a risk of complications such as rupture or infection.