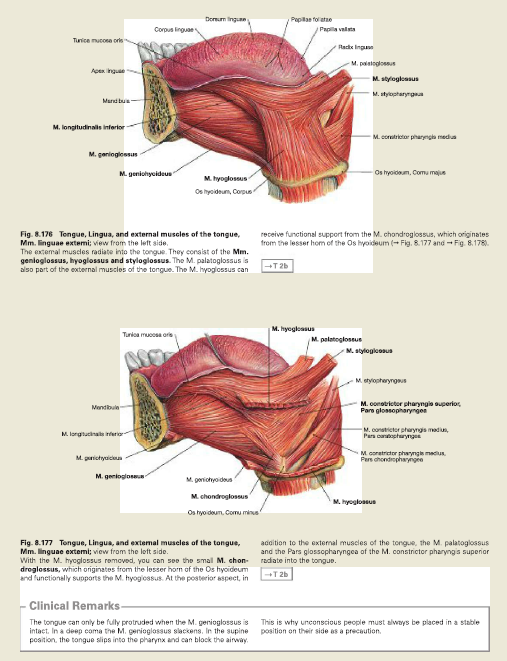
LUNG
left lung is smaller than the right because your heart is where the middle lobe on your left lung would be. Your left lung has two parts that your right lung doesn't have: the cardiac notch (where your heart fits) and the lingula, an extension of the superior lobe.
HEART
The heart is a hollow muscular pump, which lies in the middle mediastinum. On its surface, it has several distinctive features which are of anatomical and clinical importance.
In this article, we shall look at the surface anatomy of the heart and discuss the clinical relevance of these features.
Orientation and Surfaces
The heart has been described by many texts as “a pyramid which has fallen over”. The apex of this pyramid pointing in an anterior-inferior direction.
LUNG
The left lung consists of two lobes: the left upper lobe (LUL) and the left lower lobe (LLL). The right lobe is divided by an oblique and horizontal fissure, where the horizontal fissure divides the upper and middle lobe, and the oblique fissure divides the middle and lower lobes.
SPLEEN
(spleen) An organ that is part of the lymphatic system. The spleen makes lymphocytes, filters the blood, stores blood cells, and destroys old blood cells. It is located on the left side of the abdomen near the stomach.
ROOT OF LUNG
The right and left lungs differ in size and shape to accommodate other organs that encroach on the thoracic region. The right lung consists of three lobes and is shorter than the left lung, due to the position of the liver underneath it. The left lung consist of two lobes and is longer and narrower than the right lung.
ROOT OF RIGHT LUNG
Each lung is separated into lobes branching off the main bronchus; the right lung has three lobes, while the left has only two lobes. As the bronchi branch out, the total area of the two new branches is larger than its parent bronchus, making it extremely easy for the air to rush into the lungs.
KIDNEY WITH URETER
Excretion in Humans
Excretion is the process where all the metabolic wastes are removed from the body. Excretion in humans is carried through different body parts and internal organs in a series of processes.
Parotid Gland
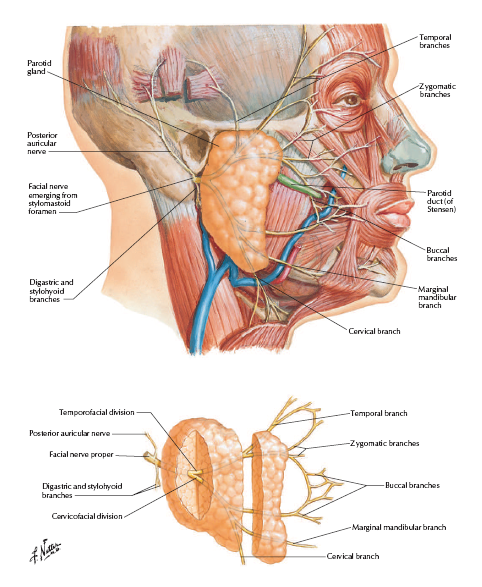
The parotid gland is a bilateral salivary gland located in the face.
It produces serous saliva – a watery solution rich in enzymes – which is then secreted into the oral cavity, where it lubricates and aids in the breakdown of food.