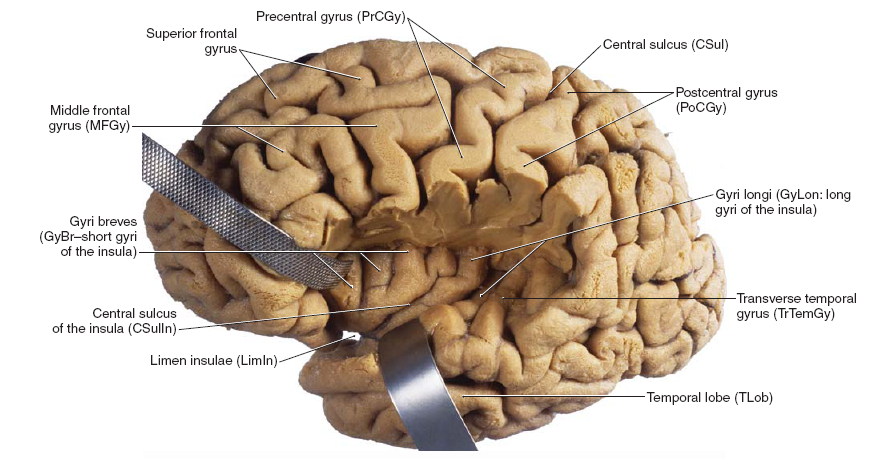
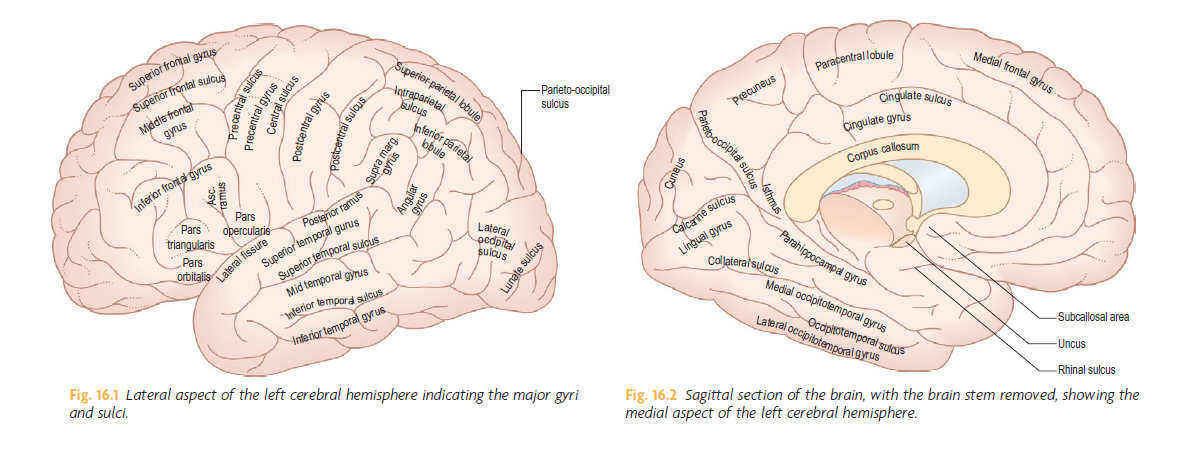
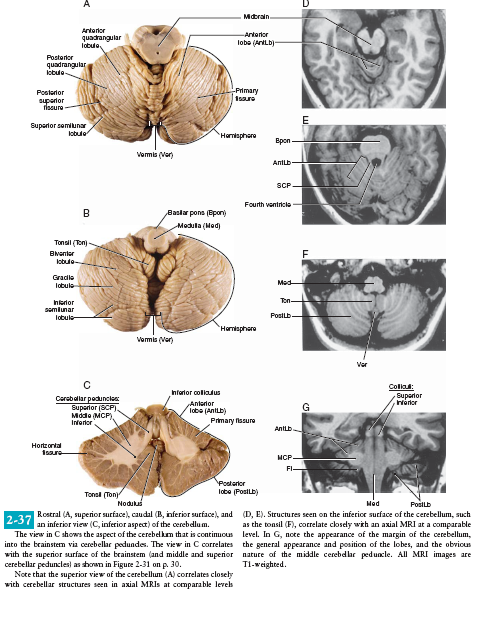
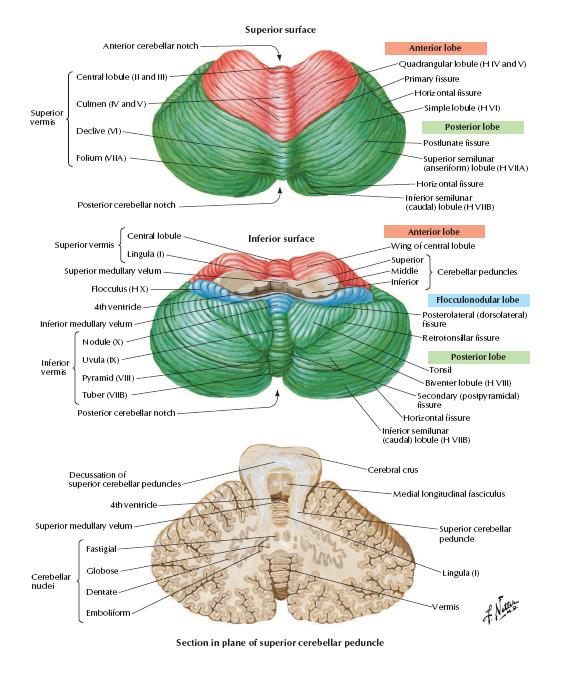
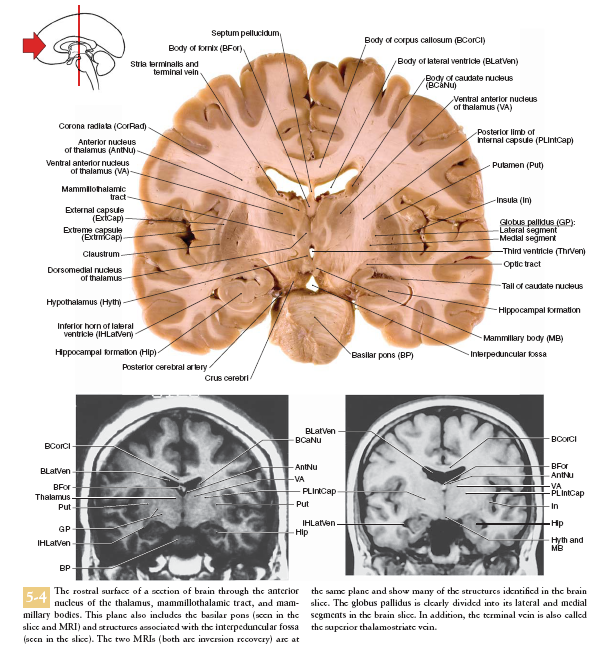
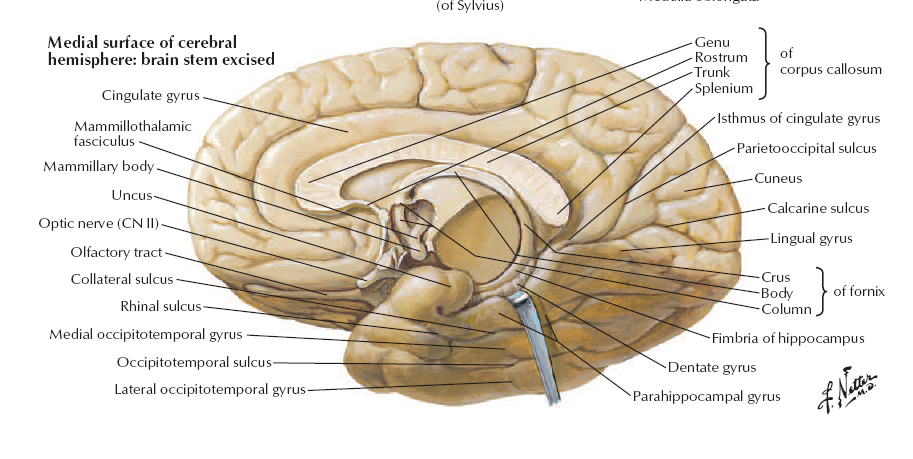
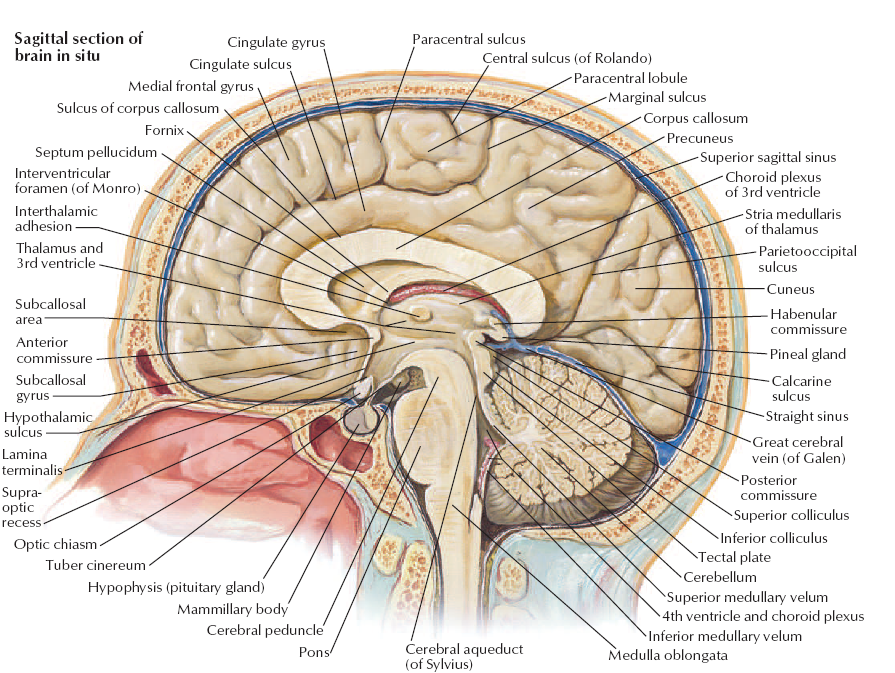
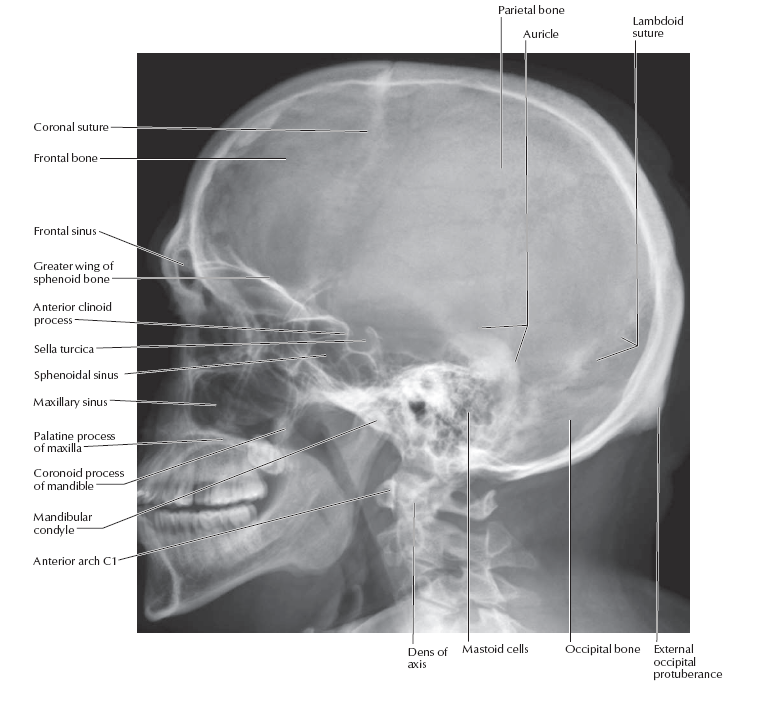
Saggital Section of Brainstem
The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. It is
sited in the posterior cranial fossa, and its ventral surface lies on the clivus.
It contains numerous intrinsic neurone cell bodies and their processes, some
of which are the brain stem homologues of spinal neuronal groups. These
include the sites of termination and cells of origin of axons that enter or leave
the brain stem through the cranial nerves. They provide the sensory, motor
and autonomic innervation of structures that are mostly in the head and
Saggital Section of Brain
https://youtu.be/2ztESvDnxT0
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord provides innervation for the trunk and limbs through the
paired spinal nerves and their peripheral ramifications. Through them it
receives primary afferent fibres from peripheral receptors located in widespread
somatic and visceral structures. It also sends motor axons to skeletal
muscle and provides autonomic innervation of cardiac and smooth muscle
and secretory glands. Many functions are regulated by intraspinal reflex connections.
Profuse ascending and descending pathways link the spinal cord with