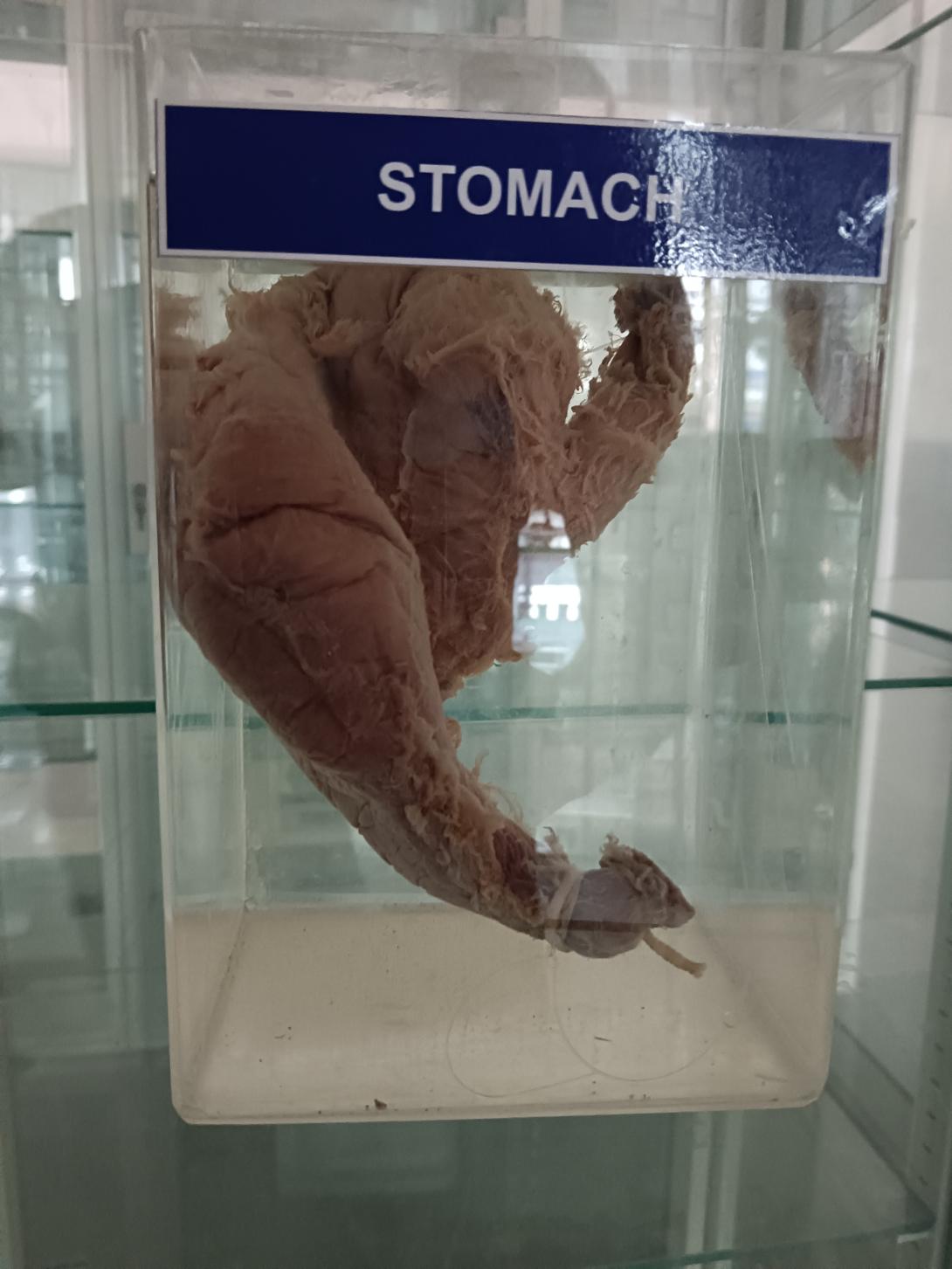
The stomach is a muscular organ located in the upper abdomen, just below the diaphragm. It is part of the digestive system and plays a crucial role in breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body.
- Cardia: This is the area of the stomach that connects to the esophagus.
- Fundus: This is the upper, rounded part of the stomach that lies above the level of the cardia.
- Body: This is the main central part of the stomach that lies between the fundus and the pylorus.
- Pylorus: This is the lower part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine.
- Lesser curvature: This is the inner curve of the stomach that faces toward the liver.
- Greater curvature: This is the outer curve of the stomach that faces toward the spleen.
- Rugae: These are the folds of the inner lining of the stomach that allow it to expand and contract as it receives and processes food.
- Gastric glands: These are the glands located in the inner lining of the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid and enzymes to aid in the digestion of food.
- Sphincters: There are two sphincters in the stomach: the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which controls the flow of food from the esophagus into the stomach, and the pyloric sphincter, which controls the flow of food from the stomach into the small intestine.
Rack Number
Specimen Number
50