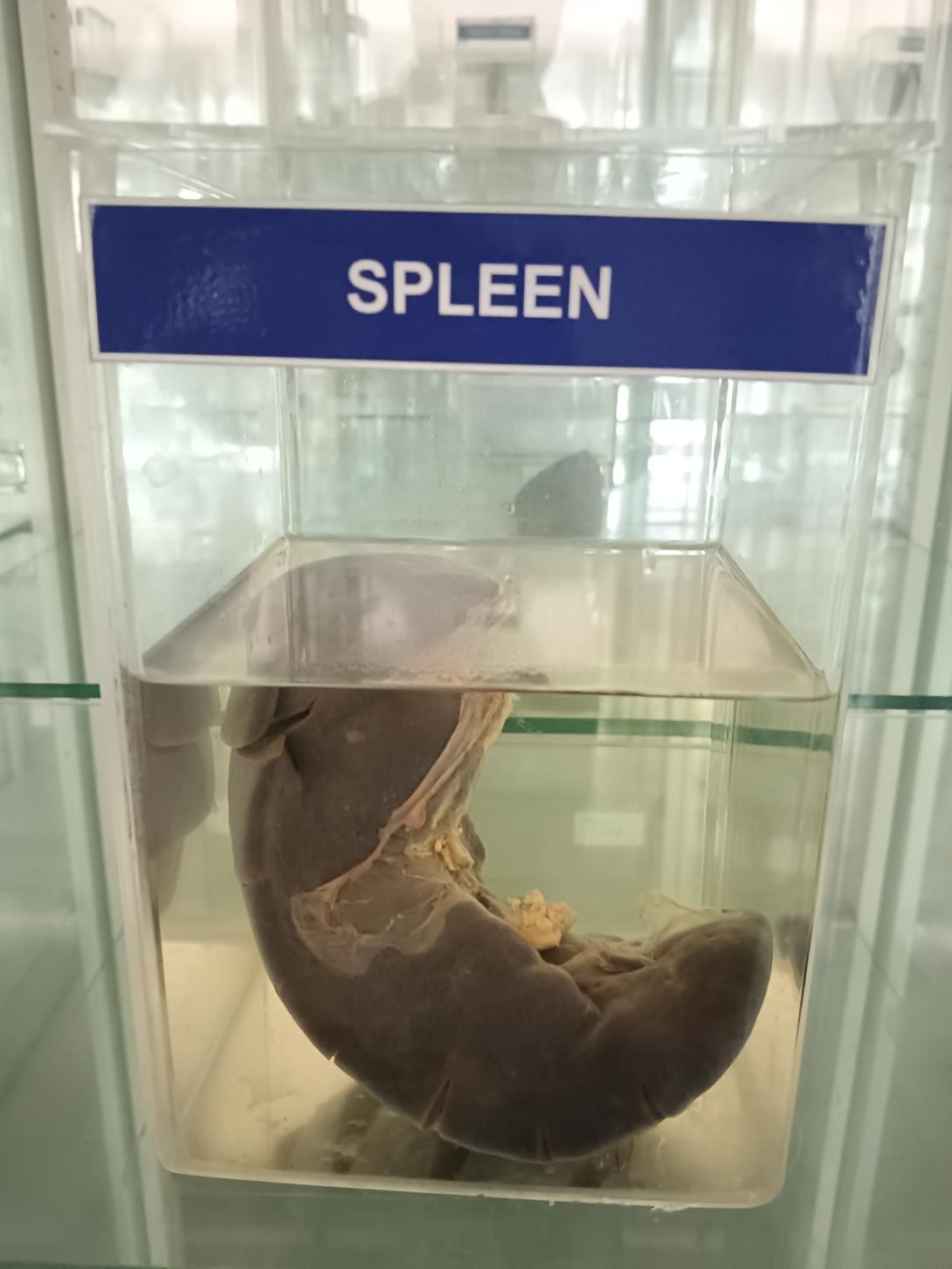
The spleen is an important organ of the lymphatic system that is located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and behind the stomach. It is a soft, purplish-red organ that is roughly the size of a fist and weighs between 150 and 200 grams.
- Capsule: The outer layer of the spleen, which is made up of connective tissue.
- Trabeculae: Thin, fibrous strands that extend from the capsule into the interior of the spleen, dividing it into compartments.
- White pulp: An area of the spleen that contains lymphoid tissue, which is important for immune function.
- Red pulp: An area of the spleen that contains blood vessels and sinuses, as well as macrophages and other immune cells.
- Splenic cords: Cords of cells within the red pulp that surround the sinuses and contain red and white blood cells.
- Hilum: The area of the spleen where the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter and exit the organ.
The spleen plays an important role in filtering blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells, and helping to fight infections. Dysfunction of the spleen can lead to various disorders, including splenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen), hypersplenism (overactive spleen), and splenic rupture (tearing of the spleen).
Rack Number
Specimen Number
46