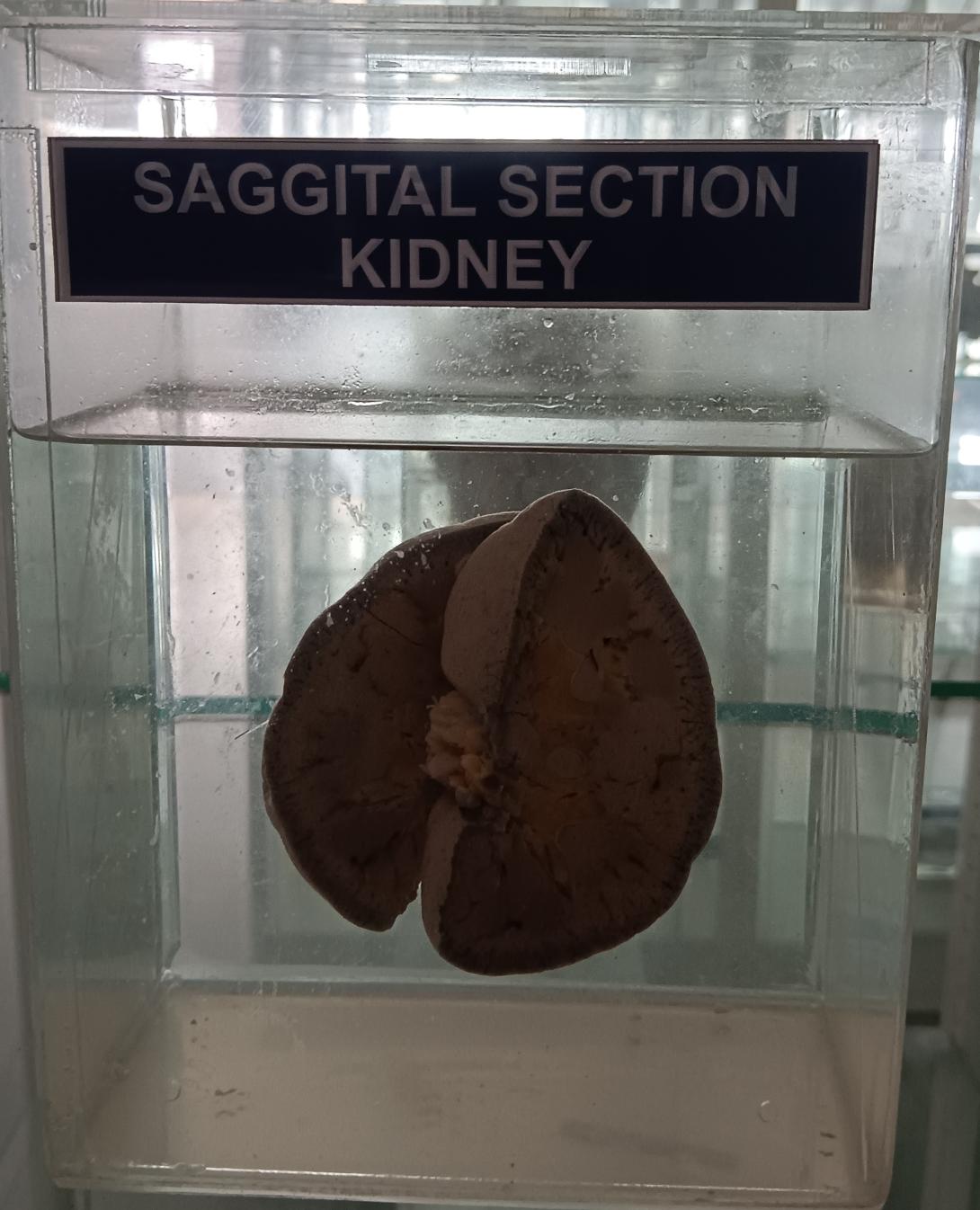
The kidneys are paired organs located on either side of the vertebral column in the retroperitoneum. Here is a brief description of the anatomy of the kidney in a sagittal section:
- Renal Capsule: The kidney is covered by a tough, fibrous capsule that helps to protect the organ.
- Renal Cortex: The outermost layer of the kidney is the renal cortex, which contains the glomeruli and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
- Renal Medulla: The renal medulla is the inner portion of the kidney, which contains the renal pyramids and the collecting ducts.
- Renal Pyramids: The renal pyramids are cone-shaped structures that contain the loops of Henle and the collecting ducts. The apex of each pyramid, called the renal papilla, points toward the renal pelvis.
- Renal Pelvis: The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped structure that collects urine from the collecting ducts and drains it into the ureter.
- Ureter: The ureter is a muscular tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
- Hilum: The hilum is a notch on the medial border of the kidney where the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter enter and exit the kidney.
- Renal Artery and Vein: The renal artery delivers oxygenated blood to the kidney, while the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidney.
- Nephron: The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and consists of the glomerulus and the renal tubule. The glomerulus filters blood, while the renal tubule reabsorbs and secretes substances to form urine.
- Perirenal Fat: The kidney is surrounded by a layer of adipose tissue called perirenal fat, which helps to protect and support the organ
Rack Number
Specimen Number
26