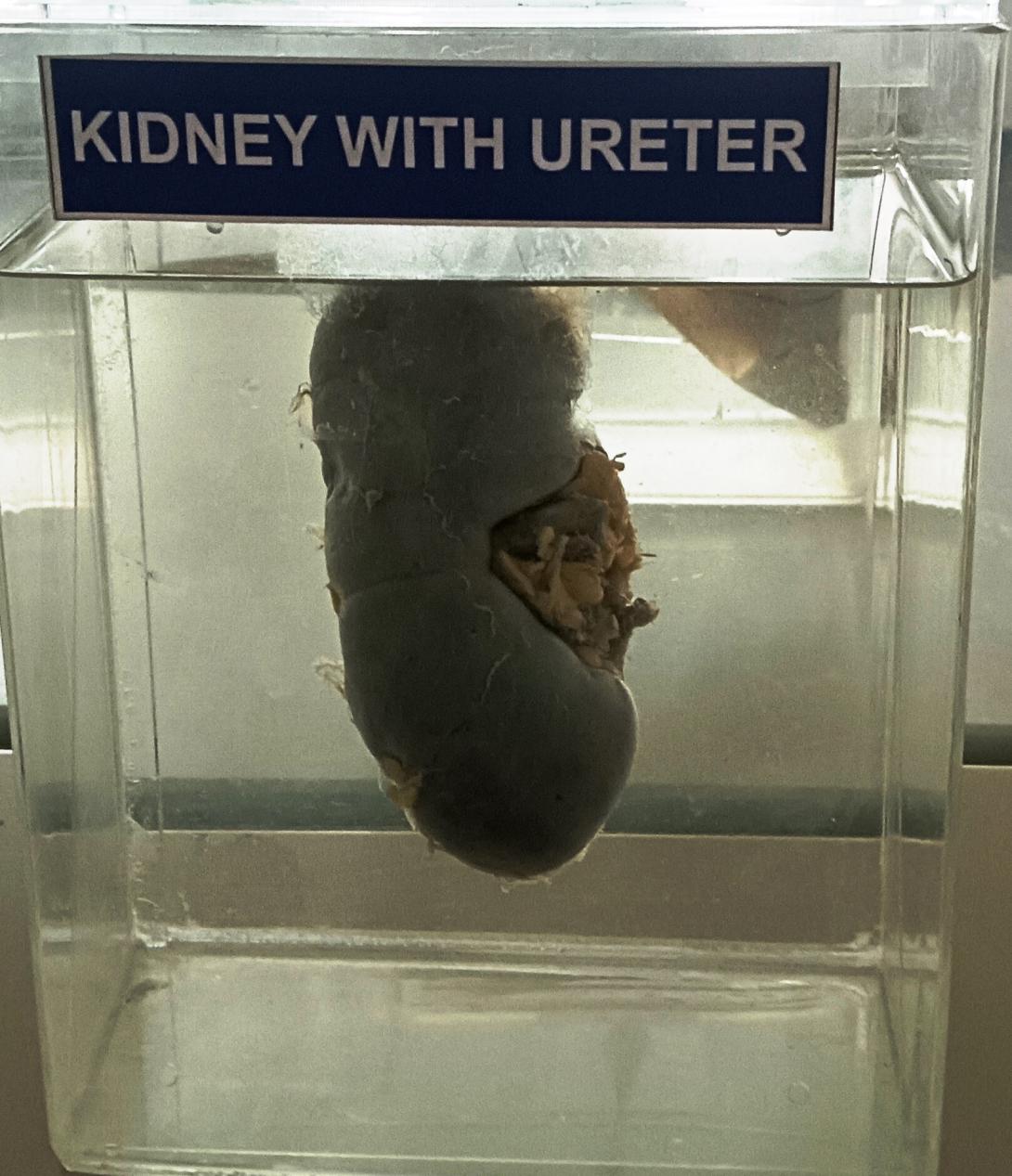
- Kidney: The kidney is a bean-shaped organ that is reddish-brown in color. It is usually about 10-12 cm in length and 5-7 cm in width. The outer surface of the kidney is smooth and shiny.
- Renal hilum: The renal hilum is a notch on the medial side of the kidney where the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter enter and exit.
- Renal cortex: The outer layer of the kidney is called the renal cortex. It appears as a thin, light-colored layer just beneath the capsule.
- Renal medulla: The inner layer of the kidney is called the renal medulla. It appears darker than the cortex and is organized into triangular-shaped sections called renal pyramids.
- Renal papilla: Each renal pyramid has a tip called the renal papilla, which projects into a funnel-shaped area called the minor calyx.
- Renal pelvis: The minor calyces merge to form the major calyces, which in turn merge to form the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped area that collects urine from the major and minor calyces and funnels it into the ureter.
- Ureter: The ureter is a muscular tube that extends from the renal pelvis to the bladder. It is about 25-30 cm long and has a diameter of about 3-4 mm. The ureter has a smooth, shiny surface and may have small, thread-like blood vessels on its surface.
- Ureterovesical junction: The ureter enters the bladder obliquely at an angle that helps prevent backflow of urine.
- Bladder: The bladder is a muscular sac that is distensible and can expand to accommodate urine. It is located in the pelvis, posterior to the pubic bone.
- Urethra: The urethra is a tube that extends from the bladder to the external urethral orifice. In males, the urethra is longer and has a prostatic, membranous, and spongy part. In females, the urethra is shorter and opens into the vestibule of the vagina.
Rack Number
Specimen Number
8