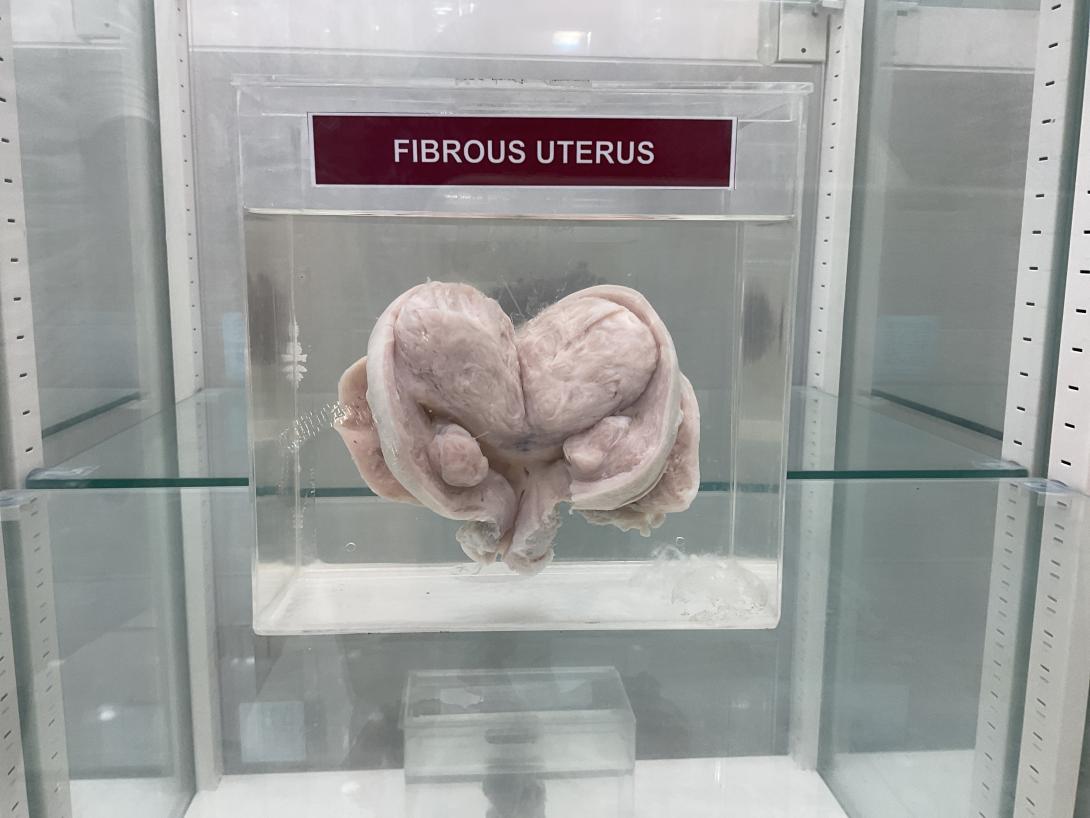
The uterus, or womb, is a pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis of a female's body. A fibrous uterus, also known as a fibroid uterus, is a uterus that contains fibroids or leiomyomas, which are benign growths that develop in the smooth muscle of the uterus. There are different types of fibroids, based on their location in the uterus:
Submucosal fibroids: These fibroids develop in the inner lining of the uterus, called the endometrium.
Intramural fibroids: These fibroids develop in the muscular wall of the uterus.
Subserosal fibroids: These fibroids develop on the outer surface of the uterus, just beneath the serosa, which is the thin membrane that covers the uterus.
Pedunculated fibroids: These fibroids are attached to the uterus by a stalk or a stem.
Fibroids can vary in size and number, and can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain, and frequent urination. Treatment for fibroids depends on the size, location, and severity of symptoms, and may include medications, surgery, or other therapies.
In addition to fibroids, other types of pathology that can affect the uterus include endometriosis, adenomyosis, and uterine polyps. Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and infertility. Adenomyosis is a condition where the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, causing pain and heavy menstrual bleeding. Uterine polyps are growths that develop in the lining of the uterus, which can cause irregular bleeding and infertility.