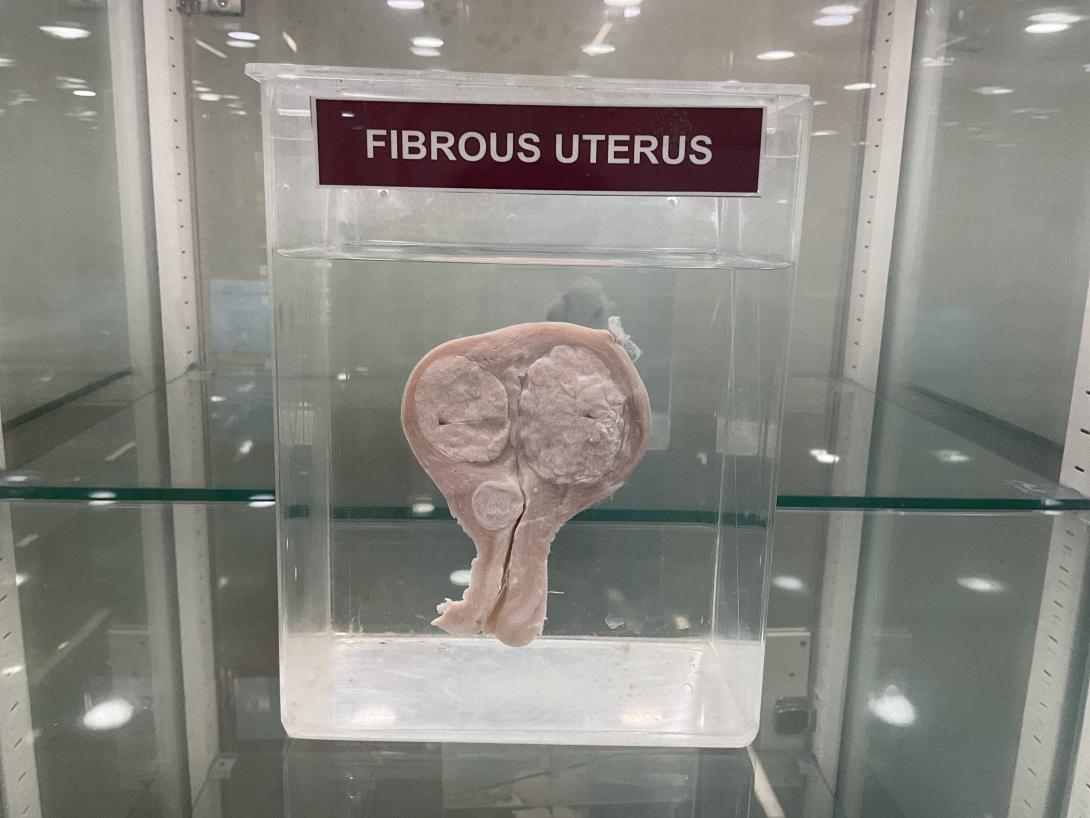
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can develop within the muscle tissue of the uterus.
The gross anatomy of the uterus affected by fibroids can include the following features:
- Size: The size of the uterus may be enlarged due to the presence of one or more fibroids.
- Location: Fibroids can develop in different locations within the uterus, including within the muscle tissue, beneath the uterine lining, or on the outside of the uterus.
- Texture: The affected area of the uterus may feel harder or more firm compared to the normal, healthy tissue due to the presence of fibrous tissue.
- Shape: The shape of the uterus may be altered, depending on the size and location of the fibroid(s).
- Symptoms: The symptoms of uterine fibroids can vary depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids, but may include heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain, abdominal discomfort, and pressure on nearby organs.
- Complications: In some cases, uterine fibroids can lead to complications, such as anemia, infertility, and problems during pregnancy and childbirth.
Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms and may include medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery to remove the fibroids or the entire uterus. It is important to note that uterine fibroids are generally benign and do not increase the risk of uterine or ovarian cancer.
Rack Number
Specimen Number
45